Governance

In the face of an increasingly severe business environment, companies cannot ignore the regulatory requirements and the climate actions brought about by global warming. PANJIT has paid long-term attention to climate change, and is dedicated to the promotion of sustainable governance. To respond to the Financial Supervisory Commission’s "Sustainable Development Roadmap" and the National Development Council’s “Taiwan’s Pathway to Net-Zero Emissions in 2050”, PANJIT refers to the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) Framework and the recommendations from Taiwan Stock Exchange Corporation Rules Governing the Preparation and Filing of Sustainability Reports by TWSE Listed Companies to assess and identify climate change risks and opportunities.
PANJIT’s ESG Promotion Office reports to the board of directors on the schedules and progress of the GHG inventory and verification schedule progress on a quarterly basis. The content of the 2023 climate-related report covers the GHG inventory progress and planning, the risk management operations (including climate change risks), etc. Through the operation of ESG Promotion Office and the reports and discussions on related climate
issues, better response strategies can be formulated to promote the sustainable management of PANJIT.

2024 Highlights of Climate-related Issues Reported to the Board of Directors

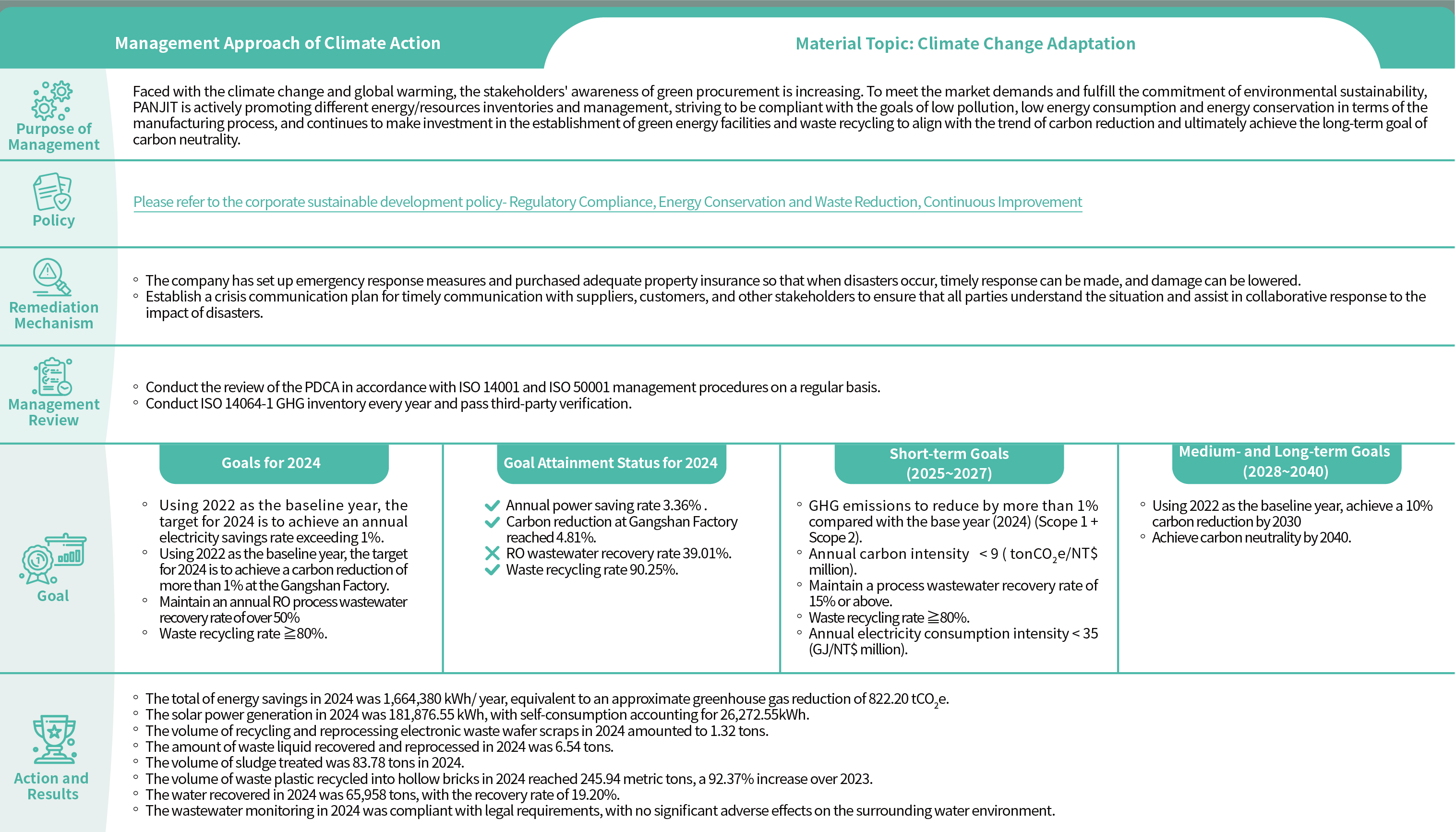
Indicator Targets
To lower the impact on operations brought by climate change, the company has set short-, medium-, and
long-term management goals for GHG emissions, renewable energy use, energy intensity management,
wastewater recycling, waste reduction and so on as the regular review and evaluation of the goal achievement status and for the establishment of corresponding improvement plans.

Climate-related Indicators


Water Resources Management



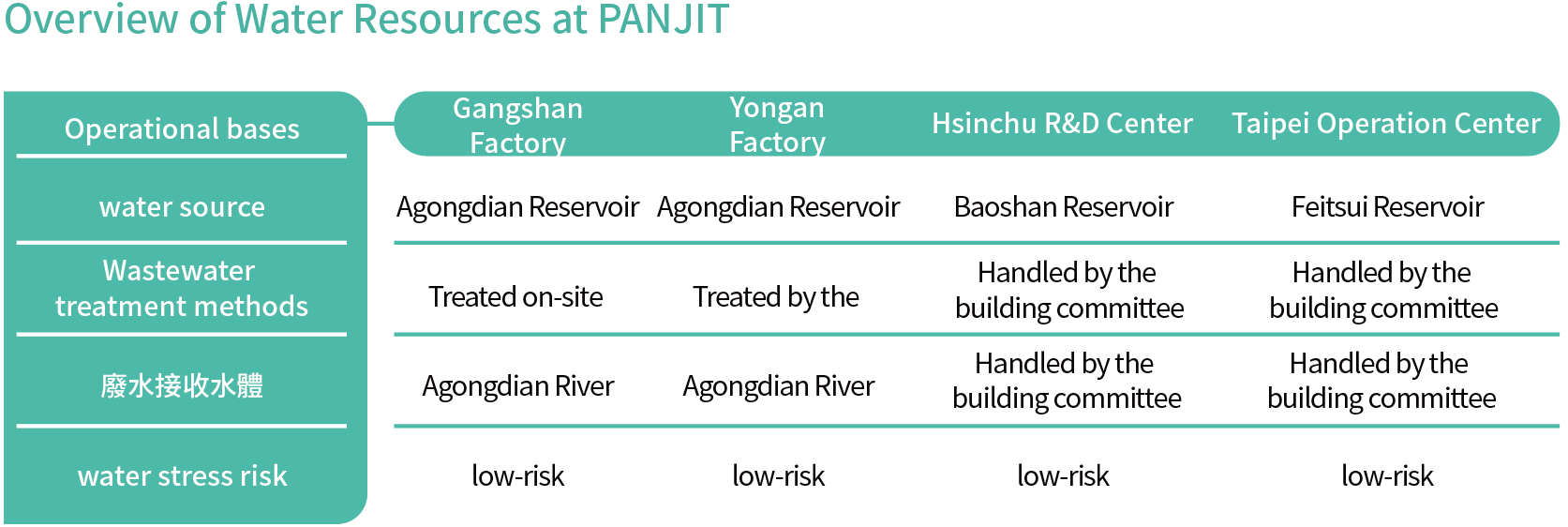
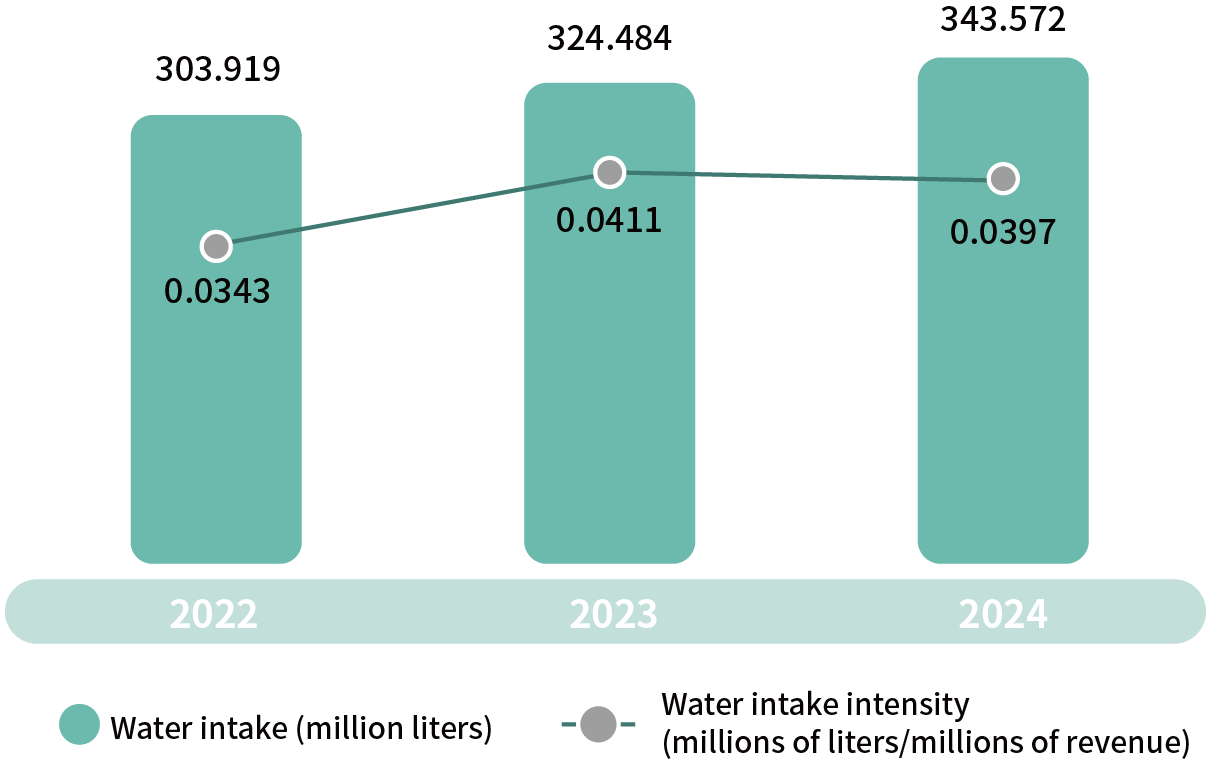
The main water use at PANJIT is tap water. Water intake is compliant with local regulations and does not cause major environmental impact. The water resource stress risk where the plant is located is assessed in accordance with the World Resources Institute’s (WRI) Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas, and the results show that PANJIT is in “low-risk” areas. The company will also continue to pay attention to the water resource risks for timely establishment of the corresponding strategies.



Wastewater at PANJIT mainly includes process wastewater and domestic sewage, which are treated onsite before being discharged, and is also diverted and managed separately in accordance with the drainage characteristics. This not only helps increase the recovery rate of water but also reduce the dosage used for water treatment that will lessen the difficulty of back-end wastewater treatment and environmental load due to the fact that some waste acid liquid and organic waste liquid still have its economic value after recovery. The treated sewage is discharged into the sewers in accordance with regulations. The company entrusted manufacturers to conduct water quality testing on a regular basis, and the results also show the treatment is compliant with legal requirements and there is no major impact on local water bodies.
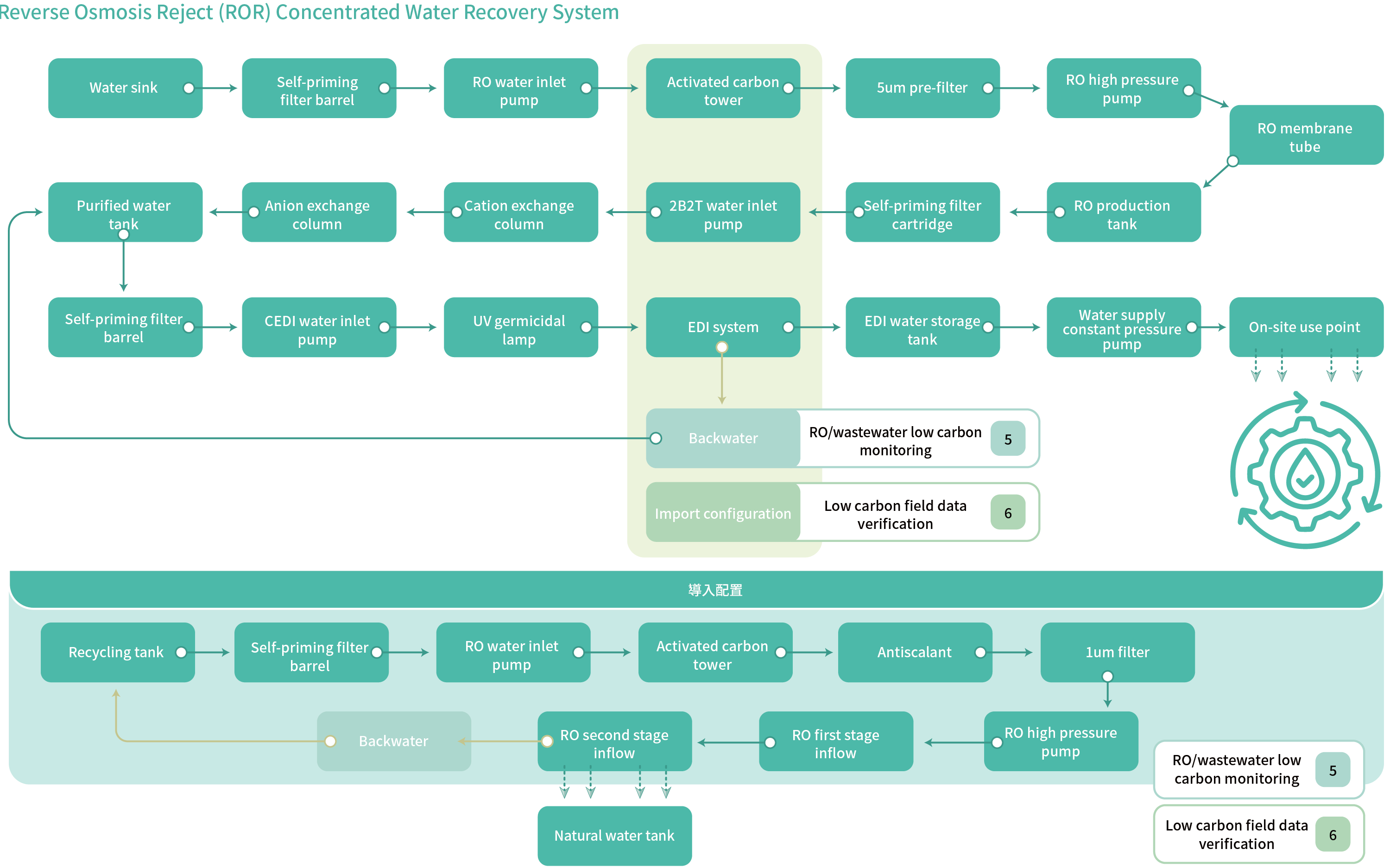
To increase the water recycling rate, the company has actively invested in the water recycling system. We have installed an electroplating-rinse-water recycling system and the dicing process wastewater recycling system in 2022 and added the recycling system for reverse osmosis (RO) concentrated water, which was commenced in 2023. It is expected to introduce digital monitoring and control in 2025 to not only observe the wastewater recycling and reuse rate, but also grasp the RO water recycling rate of each process and seek opportunities for re-optimization. The water recycled in 2024 was 65,958 tons, with the recovery rate of 19.20%. The target benchmark for the process RO wastewater recycling rate was improperly set for 2024. The original assessment mistakenly used tap water instead of the actual RO concentrated water as the benchmark, resulting in the target value being set too high. The RO wastewater recycling rate in 2024 was 39.01%.
The target value will be reassessed and adjusted based on the actual situation after one year of observation.

Waste Management

Waste at Hsinchu R&D Center and Taipei Operation Center is mainly domestic waste and is centrally managed by the office building. At Gangshan Factory and Yongan Factory, waste is divided into general industrial waste and hazardous industrial waste, and both factories entrust qualified waste disposal vendors with the waste removal and treatment. Contracts are signed and forms are submitted online. Each vendor is equipped with GPS tracking to monitor collection routes, and unannounced on-site inspections are carried out on a quarterly basis to audit the handling practices of the service
providers. E-waste and waste liquids are recovered by professional recycling companies. Recyclable waste includes general resource waste and production scrap. As part of on-site packaging reduction
efforts, cartons have been replaced by metal containers to support internal circulation and minimize the usage of both cartons and pallets. The Company's waste disposal complies with all regulations
and no hazardous waste listed in the Basel Convention is imported or exported. In 2024, there were no incidents of improper waste disposal or waste being shipped overseas for treatment.
The total waste generated in Gangshan Factory and Yongan Factory totaled 844.54 metric tons in 2024, of which 757.21 metric tons (89.66%) were general industrial waste and 87.33 metric tons (10.34%) were hazardous industrial waste. To improve resource utilization efficiency and reduce environmental impact, the Company recycled and reused a total of 682.79 metric tons of waste in 2024, accounting for approximately 80.85% of the total waste; of which a total of 40.75 metric tons of hazardous waste was recycled and reused, accounting for about 46.66% of the total hazardous waste.
Waste Reduction
PANJIT is actively implementing waste reduction management. Waste recycling awareness is strengthened in Hsinchu R&D Center and Taipei Operation Center from time to time. Yongan Factory
collaborates with recycling vendors to recover waste liquids to be reused as industrial raw materials, and a total of 6.54 tons were recycled in 2024. Gangshan Factory is actively strengthening waste recycling, conversion and reuse. The waste reduction measures and achievements of the Gangshan Plant include the followings.
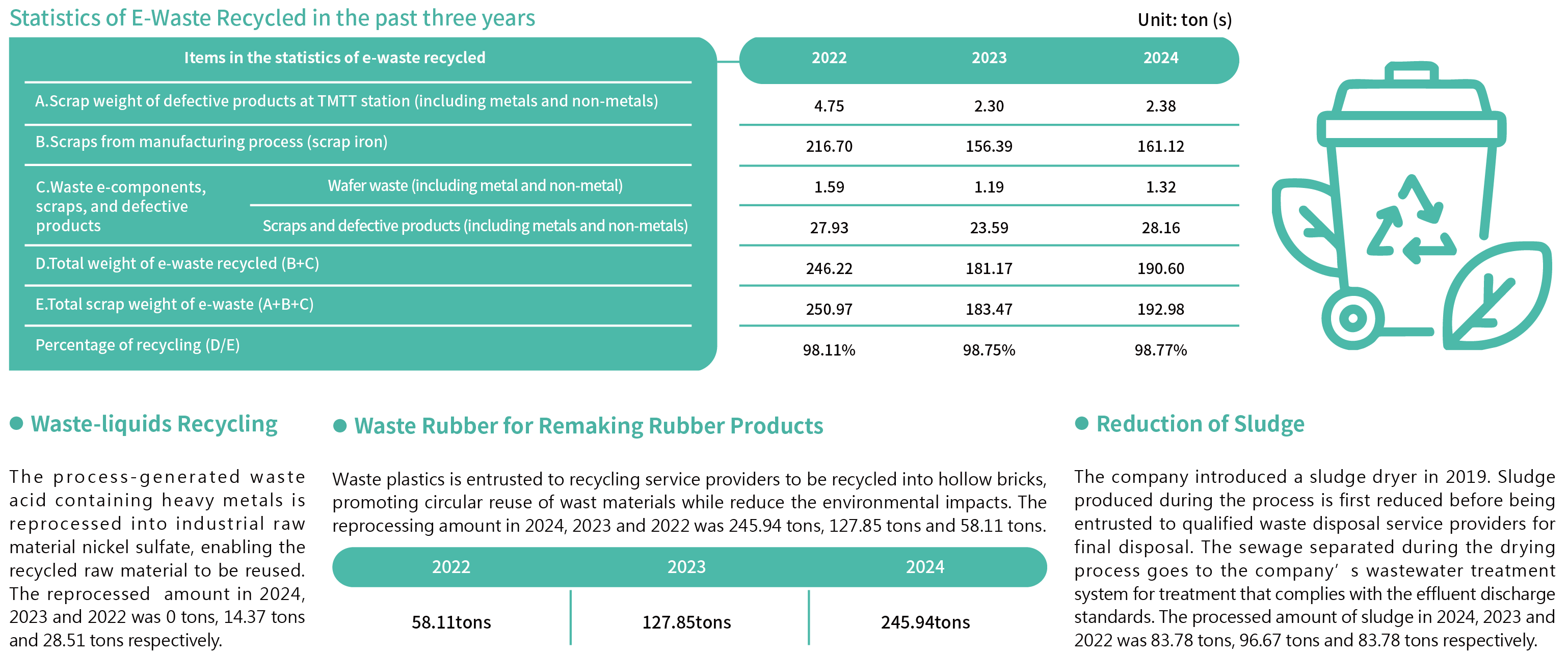
● Recycling of E-Waste:

High-purity precious metals, including gold and silver, can be refined from recycled and processed wafer scrap. The amount reprocessed in 2024, 2023 and 2022 was 1.32 tons, 1.19 tons and 1.59 tons respectively.
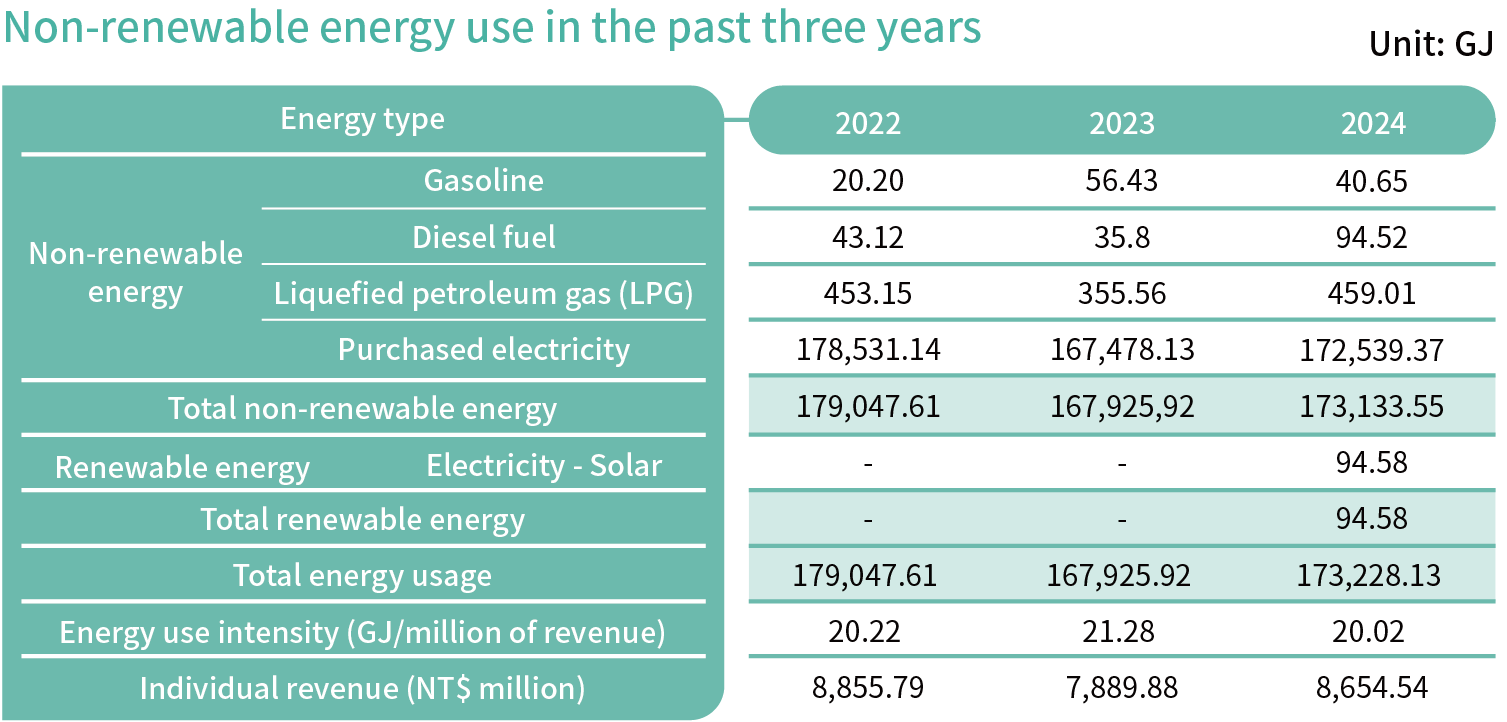

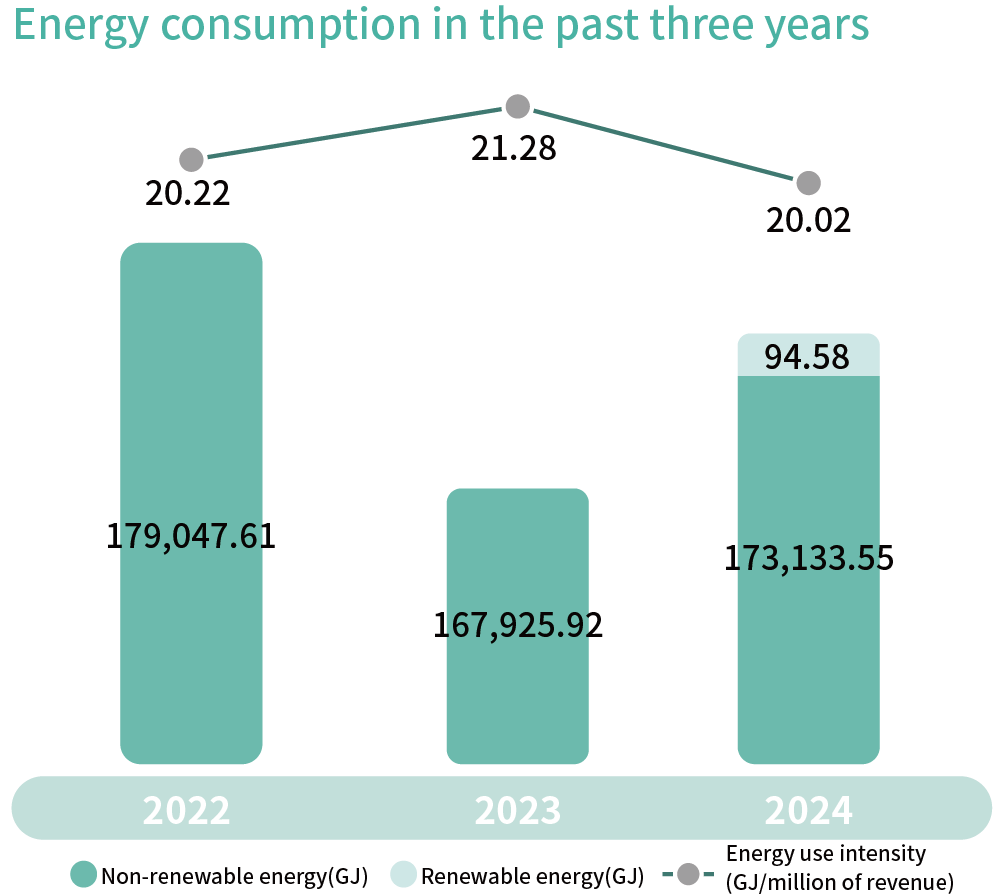
Use of Energy



The energy consumption at Gangshan Factory includes purchased electricity, gasoline, diesel, and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), among which, purchased electricity is the major energy used, accounting for 99.60% of total energy use, which is used for process power, air compressors and other electrical facilities. The remaining energy consumption is used for company cars, forklifts and cafeterias. The total energy consumption of the Gangshan Factory in 2024 was 173,228.13 GJ. To effectively manage energy use and improve energy performance, PANJIT has introduced ISO 5001 in October, 2022, and passed the verification in 2023 and 2024, showing the stability and effectiveness of the energy management system. To meet regulatory requirements, we have completed the installation of electricity and flow meters on critical energy-consuming systems, along with the deployment of real-time energy monitoring platform to drive greater efficiency and more accurate energy management.
In addition, the Company installed solar panels in the plant. In 2024, the solar installation capacity reached 183.89kW in 2024, generating a total of 181,876.55 kWh (about 654.75 GJ) of electricity, and 154.63 kW of capacity was sold in bulk to Taiwan Power Company. The 29.26 kW capacity is for self-consumption, with a total generation of 26,272.55kWh (about 94.58GJ). In the future, the Company will continue to raise the proportion of renewable energy use to achieve effective reduction of carbon emissions.
Energy conservation measures and performance
PANJIT works in line with the Ministry of Economic Affairs’project “Regulations on Setting Energy Conservation Objectives and Execution Plans for Energy Users” to promote the energy conservation plans, and a series of energy conservation actions with the goal of reaching more than 1% of average energy saving rate between 2015 and 2024. As far as PANJIT is concerned, the main energy use is from purchased electricity. Between 2023 and 2024, an energy monitoring system for plant-wide utilities (including single-system air compressors with a total power of 500 horsepower or more, with total air flow meters and independent electricity meters) was introduced. As of the end of 2024, the air compressor room's corresponding annual electricity consumption was reduced by approximately 2% (approximately eight months after the introduction), resulting in a total annual electricity savings of approximately 295,085.93 kWh/year, equivalent to a GHG reduction of approximately 145.77 metric tons of CO2e.
Note:
1. The electricity conservation data was calculated in accordance with the equipment specifications and usage scenarios.
2. The calculation of GHG reduction was conducted by using the 2023 electricity carbon emission factor of 0.494 kg CO2e/kWh announced in 2024 for conversion.

